This is a contra owner’s equity account, because it has a debit balance if draws were made. Even though it is a balance sheet account, it is a temporary account. Fees earned from providing services and the amounts of merchandise sold. Under the accrual basis of accounting, revenues are recorded at the time of delivering the service or the merchandise, even if cash is not received at the time of delivery. Things that are resources owned by a company and which have future economic value that can be measured and can be expressed in dollars. Examples include accounting formula cash, investments, accounts receivable, inventory, supplies, land, buildings, equipment, and vehicles.

How the Accounting Equation is Calculated & Applied (With Examples)
Therefore, you should always consult with accounting and tax professionals for assistance with your specific circumstances. The totals now indicate that Accounting Software, Inc. has assets of $16,300. Viewed another way, the corporation has assets of $16,300 with the creditors having a claim of $7,000 and the stockholders having a residual claim of $9,300. It will become part of depreciation expense only after the equipment is placed in service. We will assume that as of December 3 the equipment has not been placed into service. Suspense Account Therefore, there is no expense (or revenue) to be reported on the income statement for the period of December 1-3.
- Below are some examples of transactions and how they affect the accounting equation.
- Liquidity refers to a company’s ability to pay its short-term debts, while solvency refers to its ability to pay its long-term debts.
- Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program.
- The equation is generally written with liabilities appearing before owner’s equity because creditors usually have to be repaid before investors in a bankruptcy.
- CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation.
- This transaction affects both sides of the accounting equation; both the left and right sides of the equation increase by +$250.
Expense Formula
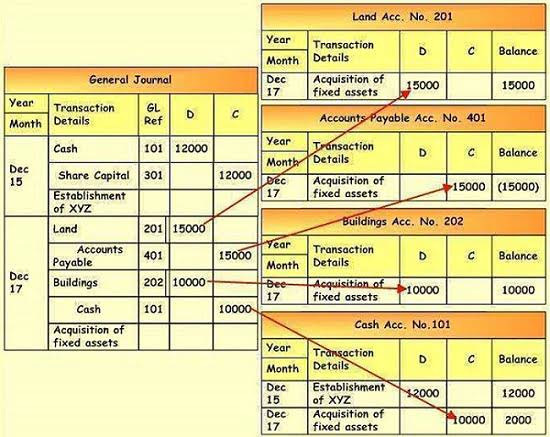
Since the amount of the increase is the same as the amount of the decrease, the accounting equation remains in balance. In our examples below, we show how a given transaction affects the accounting equation for a corporation. We also show how the same transaction will be recorded in the company’s general ledger accounts.
NY Jobs CEO Council Financial Analyst
Equity includes common stock, retained earnings, and other equity accounts. Revenue is the income earned by a company from its operations, while expenses are the costs incurred to generate that revenue. The equation states that the total assets of a business must equal the total liabilities plus the owners equity in the business. https://www.bookstime.com/ Due to this, the accounting equation is also called the balance sheet equation sometimes. Because it considers assets, liabilities, and equity (also known as shareholders’ equity or owner’s equity), this basic accounting equation is the basis of a business’s balance sheet.
In short, Apple Inc. owns $100 billion in total assets, which represents what the company controls or owns (cash, inventory, equipment, etc.). The difference, $60 billion, represents the equity or ownership interest shareholders have in the company. Losses result from the sale of an asset (other than inventory) for less than the amount shown on the company’s books. Since the loss is outside of the main activity of a business, it is reported as a nonoperating or other loss. The term losses is also used to report the writedown of asset amounts to amounts less than cost.
